Explore Azure Virtual Machines

Azure Virtual Machines (VMs) let you create and use virtual machines in the cloud. They provide infrastructure as a service (IaaS) in the form of a virtualized server and can be used in many ways. Just like a physical computer, you can customize all of the software running on the VM. VMs are an ideal choice when you need:
- Total control over the operating system (OS)
- The ability to run custom software, or
- To use custom hosting configurations
You can create and provision a VM in minutes when you select a pre-configured VM image. Selecting an image is one of the most important decisions you'll make when creating a VM. An image is a template used to create a VM. These templates already include an OS and often other software, like development tools or web hosting environments.
Moving to the cloud with VMs
VMs are also an excellent choice when moving from a physical server to the cloud ("lift and shift"). You can create an image of the physical server and host it within a VM with little or no changes. Just like a physical on-premises server, you must maintain the VM. Update the OS and the software it runs.
Scaling VMs in Azure
You can run single VMs for testing, development, or minor tasks, or group VMs together to provide high availability, scalability, and redundancy. Azure has several features so that no matter what your uptime requirements are, Azure can meet them. These features include:
- Availability sets
- Virtual Machine Scale Sets
- Azure Batch
What are availability sets?
An availability set is a logical grouping of two or more VMs that help keep your application available during planned or unplanned maintenance.
A planned maintenance event is when the underlying Azure fabric that hosts VMs is updated by Microsoft. A planned maintenance event is done to patch security vulnerabilities, improve performance, and add or update features. Most of the time these updates are done without any impact to the guest VMs. But sometimes VMs require a reboot to complete an update. When the VM is part of an availability set, the Azure fabric updates are sequenced so not all of the associated VMs are rebooted at the same time. VMs are put into different update domains. Update domains indicate groups of VMs and underlying physical hardware that can be rebooted at the same time. Update domains are a logical part of each data center and are implemented with software and logic.
Unplanned maintenance events involve a hardware failure in the data center, such as a power outage or disk failure. VMs that are part of an availability set automatically switch to a working physical server so the VM continues to run. The group of virtual machines that share common hardware are in the same fault domain. A fault domain is essentially a rack of servers. It provides the physical separation of your workload across different power, cooling, and network hardware that support the physical servers in the data center server racks. In the event the hardware that supports a server rack becomes unavailable, only that rack of servers is affected by the outage.
With an availability set, you get:
- Up to three fault domains that each have a server rack with dedicated power and network resources
- Five logical update domains
Your VMs are then sequentially placed across the fault and update domains. The following diagram shows an example where you have six VMs in an availability set distributed across the two fault domains and five update domains.
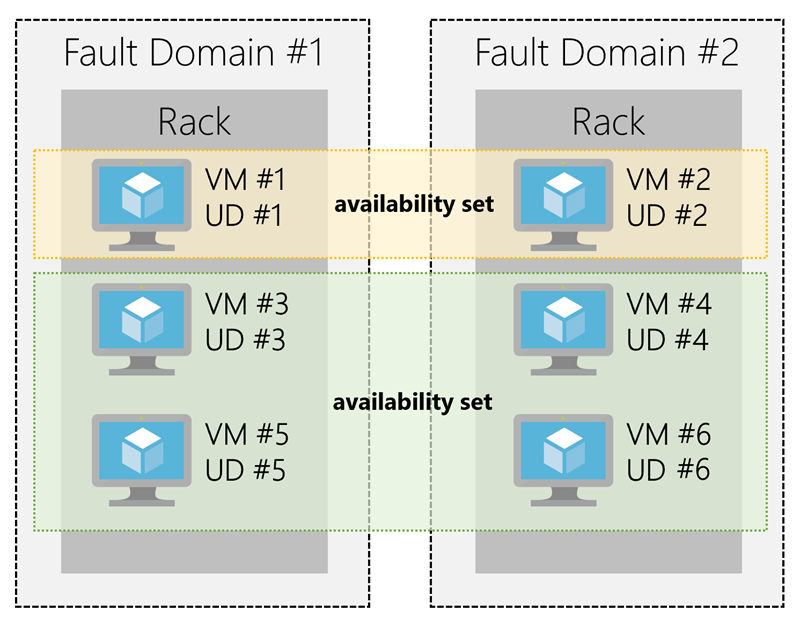
There's no cost for an availability set. You only pay for the VMs within the availability set. We highly recommend that you place each workload in an availability set to avoid a single point of failure in your VM architecture.
What are virtual machine scale sets?
Azure Virtual Machine Scale Sets let you create and manage a group of identical, load balanced VMs. Imagine you're running a website that enables scientists to upload astronomy images that need to be processed. If you duplicated the VM, you'd normally need to configure an additional service to route requests between multiple instances of the website. VM Scale Sets could do that work for you.
Scale sets allow you to centrally manage, configure, and update a large number of VMs in minutes to provide highly available applications. The number of VM instances can automatically increase or decrease in response to demand or a defined schedule. With VM Scale Sets, you can build large-scale services for areas such as compute, big data, and container workloads.
What is Azure Batch?
Azure Batch enables large-scale job scheduling and compute management with the ability to scale to tens, hundreds, or thousands of VMs.
When you're ready to run a job, Batch:
- Starts a pool of compute VMs for you
- Installs applications and staging data
- Runs jobs with as many tasks as you have
- Identifies failures
- Requeues work
- Scales down the pool as work completes
There may be situations in which you need raw computing power or supercomputer level compute power. Azure provides these capabilities.
No comments:
Post a Comment