Availability Zones
You want to ensure your services and data are redundant so you can protect your information in case of failure. When you are hosting your infrastructure, this requires creating duplicate hardware environments. Azure can help make your app highly available through Availability Zones.
What is an Availability Zone?
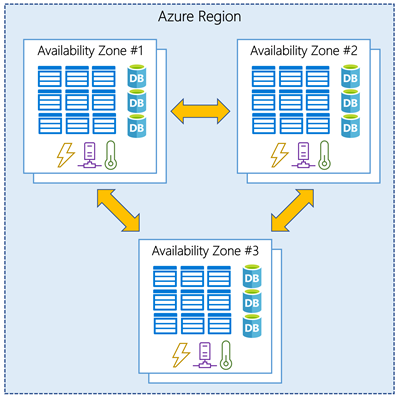
Availability Zones are physically separate datacenters within an Azure region.
Each Availability Zone is made up of one or more datacenters equipped with independent power, cooling, and networking. It is set up to be an isolation boundary. If one zone goes down, the other continues working. Availability Zones are connected through high-speed, private fiber-optic networks.
Supported regions
Not every region has support for Availability Zones. The following regions have a minimum of three separate zones to ensure resiliency.
- Central US
- East US 2
- West US 2
- West Europe
- France Central
- North Europe
- Southeast Asia
Tip
The list of supported regions is expanding - check the documentation for the latest information.
Using Availability Zones in your apps
You can use Availability Zones to run mission-critical applications and build high-availability into your application architecture by co-locating your compute, storage, networking, and data resources within a zone and replicating in other zones. Keep in mind that there could be a cost to duplicating your services and transferring data between zones.
Availability Zones are primarily for VMs, managed disks, load balancers, and SQL databases. Azure services that support Availability Zones fall into two categories:
- Zonal services – you pin the resource to a specific zone (for example, virtual machines, managed disks, IP addresses)
- Zone-redundant services – platform replicates automatically across zones (for example, zone-redundant storage, SQL Database).
Check the documentation to determine which elements of your architecture you can associate with an Availability Zone.
No comments:
Post a Comment